Preventing Soil Erosion Around Riverbank Plants
Updated June 24, 2024 at 3:21 am
Discover practical strategies to reduce erosion and protect the vital ecosystems along riverbanks by strengthening the plants that hold the soil in place, ensuring the health and stability of our waterways.
Understanding Soil Erosion and Its Impact on Riverbank Plants
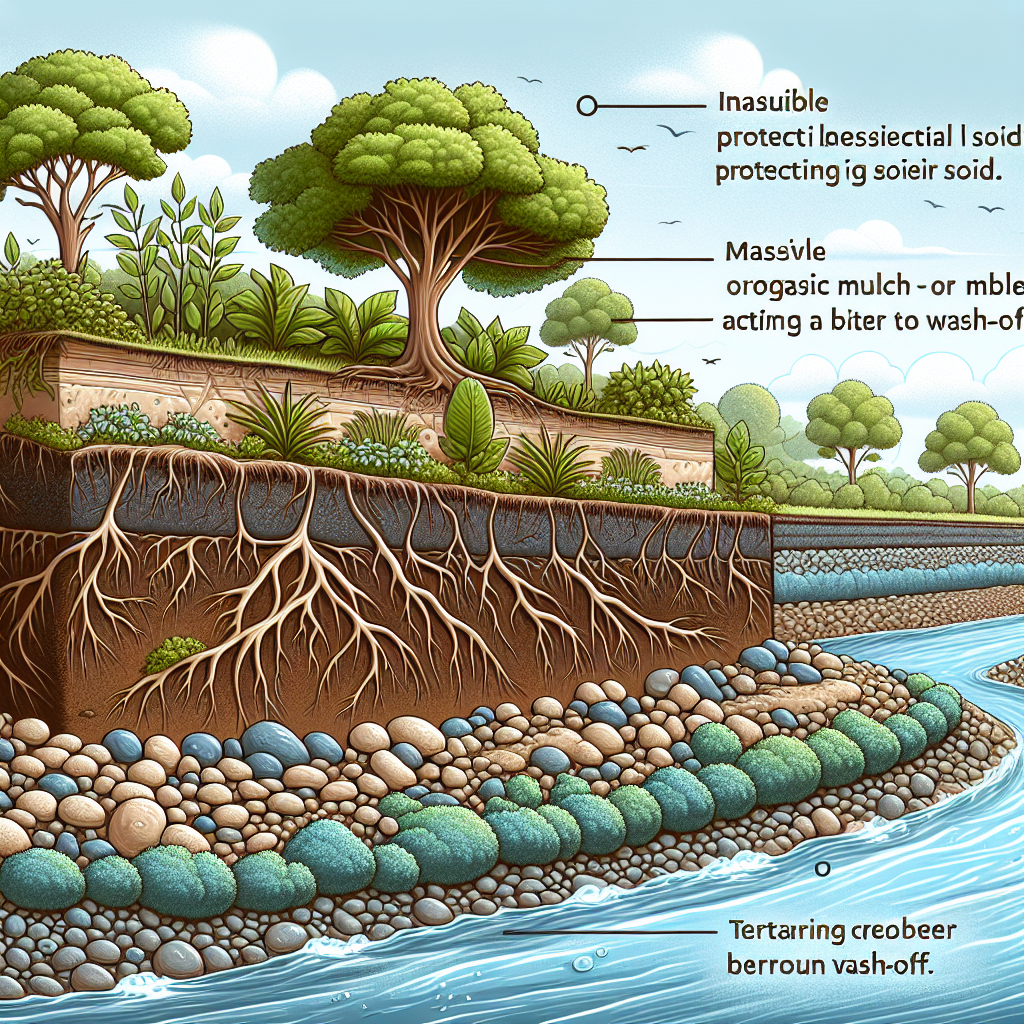
Soil erosion is a concerning environmental issue that threatens the stability and health of riverbank ecosystems. It occurs when the top layer of soil is removed, usually by water or wind. This process can have severe consequences for riverbank plants, often leading to decreased plant stability, loss of nutrients, and ultimately, plant death. But, understanding the causes and effects of soil erosion is the first step towards prevention.
When it comes to riverbanks, the constant flow of water can gradually wear away at the soil, especially when natural plant buffers are not present. This not only undermines the root systems of plants, leading to potential collapse but also contributes to water pollution and sedimentation downstream. Healthy riverbank vegetation plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of local ecosystems, providing habitat, and protecting water quality.
Identifying Vulnerable Riverbank Areas
Before you can prevent soil erosion, you need to identify which areas of your riverbank are most at risk. Look for signs of soil degradation or areas where vegetation is sparse. These are likely places where erosion is either actively happening or could happen soon.
Steep areas are particularly susceptible to erosion, as gravity can cause soil to move more quickly. Also, parts of the riverbank that experience high volumes of water flow, especially during heavy rains or floods, can be at risk. Once vulnerable areas are identified, you can begin implementing strategies for soil stabilization and plant protection.
Choosing the Right Plants to Stabilize Soil
Plant roots are incredibly effective at holding soil together and preventing erosion. When selecting plants for riverbank stabilization, opt for species that have deep, robust root systems. Native plants are usually a good choice, as they’re already adapted to the local environment and can often withstand the conditions near a water body.
Riparian plants, like willows and various species of grasses, are often recommended for erosion control due to their hardy nature and water tolerance. These plants help create a dense mat of roots that can hold the riverbank together even during periods of heavy flow. Additionally, including a mix of both deep-rooted and fibrous-rooted plants can provide surface protection and deep soil stabilization.
Implementing Erosion Control Products and Techniques
In addition to planting, there are several products and techniques designed specifically to prevent soil erosion around riverbank plants. Let’s delve into a few trusted options based on product reviews and environmental effectiveness.
Erosion Control Blankets are often used to protect newly planted areas until the vegetation has a chance to establish itself. These blankets are made from biodegradable materials, which naturally decompose over time. A popular choice is the East Coast Erosion Control Blanket. Reviews frequently mention their ease of installation and effectiveness in protecting seedlings from heavy rains. The mesh design allows the plants to grow through the blanket, creating a natural erosion barrier.
Find This and More on Amazon
Riprap, which is a layering of large stones or concrete pieces, can also protect soil from being swept away by currents. Although not a plant-based solution, when combined with vegetation, it can provide enhanced stability. The KeyRiprap technique is commonly referenced for its effectiveness in safeguarding sloped areas from erosion.
Coir Logs are another eco-friendly option commonly used to prevent riverbank erosion. Made from coconut husk fibers, these logs foster new vegetation growth and eventually degrade into non-toxic elements. The GreenStake Coir Log is praised for being both sustainable and durable. It is said that its density helps buffer areas against water flow, allowing plants to take root and flourish.
Find This and More on Amazon
Optimizing Plant Care for Erosion Prevention
Once you have chosen the right plants and implemented structural supports, proper plant care is crucial to ensure that they thrive and effectively prevent soil erosion. As with any plant, considering the specific needs of riverbank species is important.
For instance, while some riverbank plants may thrive with ‘wet feet,’ others may require well-drained soil to prevent root rot. Maintenance strategies like mulching can help maintain soil moisture and temperature, providing a favorable environment for plant growth. If you’re growing the Boston Fern for erosion control, for instance, you would want to ensure it’s planted in a shady area – as advised in the article on growing the Boston Fern for superior air purification indoors.
Practical watering techniques, including drip irrigation, can provide plants with the necessary hydration without disturbing the soil around them. Also, regular monitoring for disease and pest invasions is key to maintaining the health and integrity of the protective plant barrier.
Preventative Maintenance and Monitoring
Even with the best planning and installation, riverbank erosion control is an ongoing process. Regularly inspecting the site for signs of wear and tear, especially after heavy rains or flooding, is crucial. This includes checking your erosion control measures, such as the condition of coir logs or the stability of riprap arrangements.
If you notice areas where the soil seems to be eroding despite your efforts, it might be time to consider additional measures or alterations in your approach. For example, you may need to plant additional species or reinforce structural elements. Keeping a proactive attitude towards maintenance can save you a lot of time and resources in the long run.
Innovative Solutions to Riverbank Erosion
The field of erosion control is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques being developed regularly. For instance, the use of bioengineering methods, which combine mechanical and plant-based solutions, is becoming increasingly popular for riverbank stabilization.
One such innovative solution is the use of living walls or green walls, where plants are grown within a structural support system. This not only prevents erosion but also enhances biodiversity and aesthetic appeal. An example of this technique can be found in creating a pollinator-friendly vegetable garden, as certain structures used to attract pollinators can also contribute to erosion control.
New types of biodegradable polymers are also being used to anchor soil and release nutrients slowly, aiding plant growth. These cutting-edge methods demonstrate how creative thinking can lead to effective and sustainable solutions to environmental challenges.
Community Involvement and Education
Finally, soil erosion around riverbanks is not just an environmental concern but also a community issue. Encouraging local involvement and education in erosion prevention can amplify your efforts significantly.
Organizing community clean-up days, planting events, and educational workshops can spread awareness about the importance of riverbank health. Additionally, these activities can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards local waterways, leading to better preservation in the long term. Proper care for riverbank plants, such as nurturing ivy in low light as highlighted in nurturing ivy in low light, can serve as a gateway topic for broader environmental education activities.
Together, by understanding and addressing soil erosion, choosing robust plant life, utilizing innovative erosion control products, and fostering community involvement, valuable riverbank ecosystems can be preserved. It’s a win-win for plant life, water quality, and the well-being of all who depend on these natural resources.
Managing Water Flow and Riverbank Erosion
Effectively managing water flow is a critical aspect of preventing soil erosion around riverbank plants. Certain practices, like constructing levees, weirs, and diversion channels, can help manage the flow to minimize erosion. The use of check dams is particularly beneficial as they slow down the movement of water, which reduces its erosive power.
On a smaller scale, homeowners and land managers might employ rain gardens or buffer zones with plants to absorb excess water. Using these techniques helps to control and spread out the surge of water that can erode riverbanks during heavy rainfall events.
Understanding the Significance of Riparian Buffers
Riparian buffers are vegetated areas near water bodies that play a vital role in erosion control. A well-designed riparian buffer will include a variety of plants, from tall trees to shrubs and grasses, which work together to strengthen the soil.
Creating a riparian buffer involves planning and understanding the local ecology. Selection of the right combination of species that coexist and support each other’s growth is essential for a robust buffer. These natural barriers not only stabilize riverbanks but also provide habitat for wildlife and corridors for biodiversity.
Apply Best Practices for Land Use Planning
Developing and implementing sensible land use policies is a strategic approach to prevent soil erosion at the source. Limiting construction and deforestation near water bodies is one such policy, as it maintains the natural vegetation that protects riverbanks. Zoning laws that require setbacks for buildings from the edges of waterways can go a long way in preserving riparian zones.
Furthermore, encouraging agricultural practices that minimize runoff, such as contour farming, cover cropping, and reduced tillage, can reduce the pressure on riverbanks. Each of these methods helps keep the soil intact and prevents it from being carried away by water.
Sustainable Agriculture and Riverbank Erosion
A shift towards sustainable agricultural practices can have a positive impact on reducing riverbank erosion. Introducing perennial crops in areas where erosion is a concern is an effective strategy. These crops, with their long-lasting root systems, help hold the soil together and reduce the need for the frequent disturbance that comes with annual planting.
For example, the practice of agroforestry, which mixes trees, shrubs, and plants within agricultural land, can offer a buffer against erosion while also providing additional sources of income. Permaculture is another method that emphasizes the design of agricultural ecosystems that are sustainable and self-sufficient, further bolstering riverbank stability.
Incorporating Geotextiles in Erosion Control
Geotextiles are a product category widely used in civil engineering projects to stabilize soil and prevent erosion. These permeable fabrics, when used in conjunction with vegetation or other erosion control materials, can prevent soil displacement while allowing for water and nutrient flow.
Products like the TERRAM Geocell are gaining traction for their flexibility and durability. With geocells, you can create a three-dimensional confinement system that anchors the soil and can be planted with vegetation. Though mainly used for large scale projects, these geotextiles can also be adopted for smaller riverbank projects.
Find This and More on Amazon
Improving Irrigation and Water Usage
Efficient irrigation practices can help in managing the amount of water that reaches the riverbanks, thereby reducing erosion potential. Overwatering can weaken riverbank soil, so implementing smart irrigation systems can ensure that water is delivered only as needed.
On agricultural lands adjacent to riverbanks, switching to drip irrigation systems or soaker hoses can help minimize water runoff. Such systems deliver water directly to the plant root zones, limiting excess water that can cause soil erosion.
Mulching to Protect Soil and Plants
Mulching is a simple yet effective technique for protecting soil from erosion. A layer of mulch acts as a shield, reducing the impact of rainfall and runoff. Organic mulches, such as straw, bark, or wood chips, not only slow down water but also contribute to soil health as they decompose.
For riverbank plants, mulching can provide additional benefits by maintaining soil moisture and regulating temperature, which is especially useful for plants like the spider plant that prefer consistent moisture without being waterlogged, as discussed in the article on enhancing indoor air quality with spider plants.
Building Strong Networks with Environmental Organizations
Collaborating with environmental organizations can be a powerful way to tackle riverbank erosion effectively. These organizations often have access to resources, expertise, and volunteers that can assist in large-scale erosion control projects.
Partnerships with local conservation groups, government agencies, and universities can lead to more well-rounded and successful strategies. Engaging with experts can also provide opportunities to learn about the latest research and best practices in erosion prevention.
Leveraging Technology for Monitoring and Intervention
Technology plays a crucial role in monitoring soil erosion and providing timely interventions. Tools like GIS mapping and remote sensing can help identify erosion hotspots and track changes over time.
Drones are increasingly being used to survey and monitor riverbanks, giving a bird’s eye view of the areas that are at risk. By leveraging these technologies, interventions can be planned and implemented more strategically, ensuring effective erosion control measures are in place.
Regular Education and Training Sessions on Erosion Control
Educating residents and landowners about the importance of soil conservation and erosion control is integral to long-term success. Regular training sessions can empower individuals with the knowledge and skills to address erosion issues on their properties.
Topics such as the selection of appropriate plant species, installation and maintenance of erosion control products, and sustainable land management practices can be covered. By educating the community, a more proactive and informed approach to erosion control can be cultivated.
Adopting Contour Farming and Terracing
Contour farming and terracing are agricultural techniques that can be modified for use around riverbanks to combat soil erosion. By following the natural contours of the land and constructing terraces, water flow is slowed down, which significantly reduces the erosive energy of surface runoff.
This landscaping method is particularly useful on sloped riverbanks, where the terrace acts like a natural barrier, spreading water more evenly and providing a stable area for plants to grow. This not only minimizes erosion potential but also creates a visually pleasing tiered effect on the landscape.
Retrofitting Existing Structures
In cases where structures already exist near riverbanks, retrofitting may be necessary to prevent further soil erosion. This can involve reinforcing the foundations with erosion-resistant materials or incorporating vegetation strategically around the structure.
For example, if there is a patio near a riverbank, planting erosion-resistant shrubbery around its edges can protect the soil from runoff. Sometimes, additional features like a French drain system can aid in directing water away from vulnerable areas.
Considering Climate Change Impacts
Climate change has the potential to exacerbate soil erosion problems, with increased frequency and intensity of storms leading to higher runoff and erosion rates. Riverbank stabilization efforts need to account for these likely changes in weather patterns.
Plants selected for erosion control must be resilient to changing climatic conditions. This might mean choosing species that can tolerate both drought and floods or implementing more robust infrastructural solutions that can withstand extreme weather events.
Final Thoughts on Preserving Riverbanks
Preserving riverbanks from erosion is a multifaceted task that requires a mix of practical measures, community involvement, and forward-thinking. By employing a combination of vegetation, structural solutions, sustainable practices, and technologies, the integrity of riverbank ecosystems can be maintained for future generations.
Remember, every action taken to prevent soil erosion not only contributes to the preservation of riverbank plants but also ensures cleaner waterways, healthier wildlife habitats, and a more resilient environment against the effects of climate change and human activities.
.
Shop more on Amazon
Flowers & Plants Team
Flowers & Plants Team


