Protecting Grapevines from Pests and Diseases
Updated July 3, 2024 at 12:18 pm

Understanding Pest and Disease Management in Grapevines
- Eco-friendly: Uses sustainable approaches that minimize harm to the environment, beneficial insects, and non-target species.
- Application Methods: Includes a variety of techniques such as spraying, biological controls, and cultural practices to manage pests and diseases.
- Resistance Management: Involves alternating chemicals or using mixed treatment strategies to prevent pests and diseases from developing resistance.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Considers the most efficient use of resources to achieve control without unnecessary expenses.
- Long-term Outlook: Emphasizes the importance of maintaining healthy vines over time, not just quick fixes.
Identifying Common Vineyard Pests and Their Control
Vineyards are often susceptible to a host of pests, including insects, mites, and larger animals. Some common pests are grape leafhoppers, Japanese beetles, and spider mites. Each pest has its own set of preferred conditions and treatment methods. For instance, grape leafhoppers can be managed through the application of insecticidal soaps or oils, which are especially effective when used early in the season.
Japanese beetles, on the other hand, can be hand-picked off vines early in the morning or controlled with pheromone traps. Spider mites require a watchful eye, as outbreaks are often related to the use of broad-spectrum pesticides that kill off their natural predators. Miticides or oils can be a part of integrated pest management strategies used to control mites.
Fighting Diseases in Grapevines: Key Strategies
Fungal diseases pose a significant threat to grapevines, with powdery mildew and downy mildew being particularly troublesome. Powdery mildew can be addressed through sulfur-based fungicides or by planting resistant varieties. Downy mildew management consists of a rotation of fungicides that belong to different chemical groups to avoid resistance buildup, and sprays should be timed to protect the vines during periods of high humidity.
Another major disease is botrytis bunch rot, commonly controlled by canopy management practices that promote air circulation. Fungicides specifically designed to target botrytis, such as products containing the active ingredient cyprodinil or fenhexamid, can be highly effective, especially when applied as the grapes begin to ripen.
Chemical-Free Approaches to Protecting Your Vines
Cultural practices can significantly reduce the incidence of pests and diseases in grapevines. Maintaining a clean and well-pruned vineyard allows for better air circulation and sunlight penetration, which can inhibit the growth of fungi. In addition, cover cropping and promoting biodiversity with beneficial insects can create a more balanced ecosystem that naturally keeps pest populations in check.
Another important measure is to select disease-resistant grape varieties, which can greatly reduce the reliance on chemical controls. For vineyards looking to minimize their chemical footprint, these resistant varieties can offer an excellent foundation for a more sustainable approach to vineyard management.
Integrating Biological Controls in Grapevine Health
Biological control involves using natural predators, parasites, or pathogens to manage pest populations. For example, the release of predatory insects like ladybugs or lacewings can help control aphid populations in the vineyard. Beneficial nematodes are another option used against soil-dwelling insect larvae.
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a bacterial soil-dweller known to control caterpillar populations that may damage grape leaves. It’s a selective pesticide that poses minimal risk to humans, animals, and beneficial insects, making it a cornerstone of integrated pest management in organic vineyards.
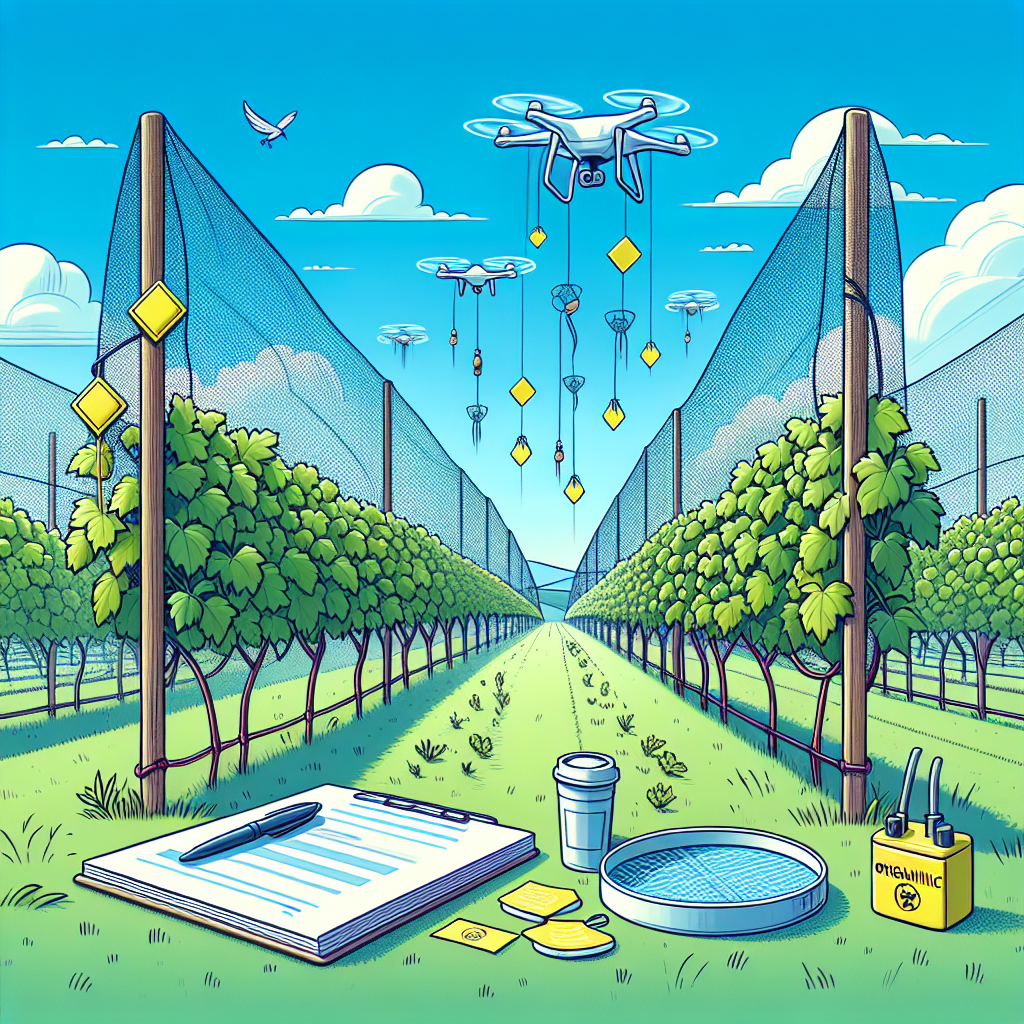
Advances in Technology for Vineyard Management
Modern vineyard management has benefited significantly from technological advancements. Precision agriculture tools, such as drones or satellite imagery, can help in early detection of pest hotspots or nutrient deficiencies. These technologies allow for targeted applications of treatments, reducing overall chemical use and ensuring that interventions are made as efficiently as possible.
On the smaller scale, robust mobile applications can help vintners keep detailed records of pest and disease pressures, weather patterns, and treatment outcomes. Such data accumulation is invaluable for fine-tuning vineyard practices and planning for long-term sustainability.
Understanding Vineyard Soil Health and Its Impact on Grape Quality
The health of vineyard soil is a critical factor in the overall health of grapevines and the quality of grapes produced. Healthy soil supports a robust population of microorganisms that can help suppress soil-borne diseases. Additionally, well-balanced soil provides the necessary nutrients for grapevines to thrive and defend themselves against pests and diseases naturally.
A key to maintaining soil health is regular testing and amendment based on test results. Organic matter, such as compost, can improve soil structure, water retention, and microorganism diversity. Soil cover crops can also play a role in managing pests by providing habitat for beneficial insects and improving soil health.
Preventing Pest and Disease Spread with Quarantine and Sanitation Measures
A strong defensive strategy against the spread of pests and diseases involves quarantine and sanitation measures. This may involve removing and properly disposing of infected plant material, sanitizing tools and equipment after use, and controlling the movement of machinery and people between vineyards to prevent cross-contamination.
Proper sanitation practices can also extend to the post-harvest handling of grapes. Facilities where grapes are processed should be kept clean to prevent the development and spread of spoilage organisms that can degrade grape quality and wine flavor profiles.
Selecting and Using Pesticides Responsibly in Grape Culture
When chemical interventions become necessary, selecting and using pesticides responsibly is paramount to protect the environment and non-target species. Always reading and following label instructions exactly as specified ensures the effectiveness of the product and reduces risks. Use the minimum effective dose and apply during times when beneficial insects are not active.
Systemic pesticides can provide longer-lasting protection, but they should be used judiciously. For example, products like imidacloprid, which are neonicotinoids, can be effective against various vineyard pests when used correctly. However, they have come under scrutiny for their potential effects on pollinators, so alternatives should be considered if possible.
Find This and More on Amazon
Practical Tips for Routine Monitoring and Vineyard Scouting
Regular monitoring and scouting of the vineyard are essential for early detection of pests and diseases. This involves walking through the vineyard, examining plants, and keeping records of any issues found. Knowing what to look for, such as discolored leaves or stunted growth, can help identify problems before they escalate.
Digital tools may also assist in vineyard scouting. Apps can now streamline the monitoring process, allowing viticulturists to log sightings of pests or symptoms of disease immediately, creating a comprehensive health record for the vineyard over time.
Community Involvement for Area-Wide Pest and Disease Management
Pest and disease management is most effective when applied on a larger, community scale. Engaging with neighboring vineyards and regional viticulture associations can help coordinate efforts to control outbreaks that would be difficult to manage by individual growers alone.
Sharing insights and strategies, such as the timing of sprays or the discovery of resistant vine strains, can benefit the entire community. Participating in workshops and seminars keeps growers informed and promotes proactive, rather than reactive, management strategies.
The Role of Climate and Weather in Grapevine Pest and Disease Management
Climate and weather play a significant role in the prevalence of pests and diseases in grapevines. Warmer temperatures may increase the range and activity level of certain pests, while rainy periods can encourage fungal diseases. Understanding these patterns can help in planning targeted pest and disease control measures.
Weather prediction models and climate data can inform when to apply protective sprays or take other preventive actions. Additionally, climate-smart agriculture, including the adoption of drought-resistant rootstocks and the use of shade cloths, can help mitigate the impact of climate change on pest and disease pressures.
Educating Customers and the Public on Sustainable Vineyard Practices
Education is a powerful tool for promoting sustainable vineyard practices. By informing customers and the public about the efforts made to manage pests and diseases responsibly, vineyards can build trust and support for their brand. Transparency in practices can also lead to consumer advocacy for more eco-friendly wine production methods.
Vineyards can host tours, wine tastings, and workshops to directly engage with their audience. Educational materials, such as brochures and websites, can further communicate the commitment to sustainable growing techniques and the benefits these practices have on the final product.
Future Trends in Vineyard Pest and Disease Management
As the wine industry continues to evolve, so will the approaches to pest and disease management. Current trends suggest an increasing move towards precision viticulture, biological controls, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) designed for resistance to specific threats.
Research into natural plant defenses and breeding for natural resistance to pests and diseases is ongoing and holds promise for future vineyard sustainability. The integration of next-generation technology will continue to shape best practices in this area, potentially transforming traditional approaches.
Optimizing Grapevine Health with Proper Nutrition and Fertilization
Just like any other plant, grapevines require a specific balance of nutrients to stay healthy and productive. A vine that has all the nutrients it needs is more capable of resisting pests and diseases. To this end, a well-planned fertilization program that replenishes the soil with essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and various micronutrients is key.
Soil tests are invaluable in determining the specific nutritional needs of your vines. Organic fertilizers, such as compost and manure, can also add nutrients while improving soil structure. Remember that excessive fertilizer can lead to lush growth that is more susceptible to pests and diseases, so moderation is crucial.
Creating a Supportive Ecosystem with Companion Planting
Companion planting can be a natural way to boost your grapevines’ defense against certain pests and diseases. Planting certain flowers and herbs around the vineyard can attract beneficial insects and even repel harmful ones. For example, marigolds have been known to deter nematodes and whiteflies, while basil can help to repel thrips and flies.
By creating a diverse plant environment, you not only reduce the reliance on chemical pesticides but also support a healthy vineyard ecosystem. Plus, the addition of companion plants can increase the aesthetic appeal of your vineyard and might add another layer of enjoyment for visitors.
Managing Vineyard Biodiversity for Healthier Vines
A biodiverse vineyard is one that has a variety of organisms living in balance, from microorganisms in the soil to insects in the foliage. Encouraging beneficial species that prey on harmful pests can significantly reduce the need for chemical interventions. For instance, encouraging birds and bats to the area can help control insect populations naturally.
Biodiversity isn’t just beneficial for pest management; it also contributes to soil health and vine vitality. Establishing hedgerows and maintaining natural areas within and around vineyards can be pivotal in fostering this balance.
The Interplay Between Vine Training and Disease Management
The method and system of vine training can have a profound effect on the airflow and sun exposure around grape clusters, impacting disease susceptibility. Training systems that allow for open canopies can enhance sunlight penetration and air circulation, reducing the risk of fungal diseases. Adjusting trellis systems and vineyard row orientation are just a couple of ways to achieve this.
Selecting an appropriate training system goes hand-in-hand with the specific conditions of your vineyard, including grape variety, climate, and topography. The right configuration can make all the difference in promoting healthy, high-quality grapes.
Insights into Organic and Biodynamic Viticulture
Organic and biodynamic viticulture puts a strong emphasis on maintaining the ecological balance and minimizing external inputs. Organic vineyards, for instance, shun synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, focusing instead on natural alternatives like composting and organic sprays.
Biodynamic practices go even further, integrating cosmic rhythms and preparations from herbal and mineral substances. Although these methods may not be for everyone, they have passionate followers, and some swear by the influence these practices have on the character and taste of the wine produced.
Keeping Ahead of Resistance: The Importance of New Product Development
Resistance is a continual battle in the world of pest and disease management. Pests and pathogens can quickly build up resistance to widely used products, rendering them less effective over time. That’s why the constant development of new products and active ingredients is crucial.
New products not only harness novel modes of action that pests haven’t encountered before, but they can also offer more specific targeting, which reduces their environmental footprint. Staying informed about the latest releases can put you at the forefront in the fight against resistance.
Navigating the Complex World of Vineyard Pest and Disease Regulations
Regulations for managing vineyard pests and diseases can be complex, varying by region and even year to year. Staying compliant not only ensures legal operations but also promotes safety and product quality. This might entail adhering to restrictions on specific chemicals, complying with quarantine measures, or completing certification processes.
Keeping up to date with local and national regulations and maintaining good communication with agricultural extension services can make navigating these complexities much smoother. It’s also a means of demonstrating to your clientele your commitment to responsible viticulture.
Communal Efforts in Research and Knowledge Sharing for Vine Health
Research into vineyard pest and disease management is ongoing and dynamic. Collaborations between universities, research institutions, and grape growers have resulted in significant advancements in this field. Areas of study include breeding disease-resistant grape varieties, developing environmentally friendly pest control methods, and uncovering the nuances of vine biology.
Participating in research programs or contributing to communal knowledge sharing platforms can enhance your understanding of vine health management. Moreover, it can provide opportunities to benefit from cutting-edge science and adopt practices that may give your vineyard a competitive edge.
Final Thoughts on Protecting Grapevines from Pests and Diseases
Protecting grapevines from pests and diseases is a multifaceted task that requires vigilance, adaptability, and a commitment to sustainable practices. By understanding the tools and strategies at your disposal, you can create a more resilient vineyard with healthier vines and better-quality grapes. Whether utilizing the latest technological advancements or embracing time-tested techniques, your efforts contribute not only to the success of your vineyard but to the broader goal of environmental stewardship in agriculture.
With the right combination of knowledge, skills, and dedication, you can overcome the challenges posed by pests and diseases and look forward to bountiful, delicious harvests for years to come.
Shop more on Amazon