Kudzu Invasion: Identifying and Controlling This Aggressive Plant
Updated June 13, 2024 at 8:59 pm

Understanding the Kudzu Invasion
Kudzu, also known as Pueraria montana, is a climbing, coiling, and trailing vine native to Asia. Brought to the United States in the late 1800s for ornamental gardens and later for erosion control, this perennial plant has since become a symbol of unbridled nature’s takeover in various parts of the country.
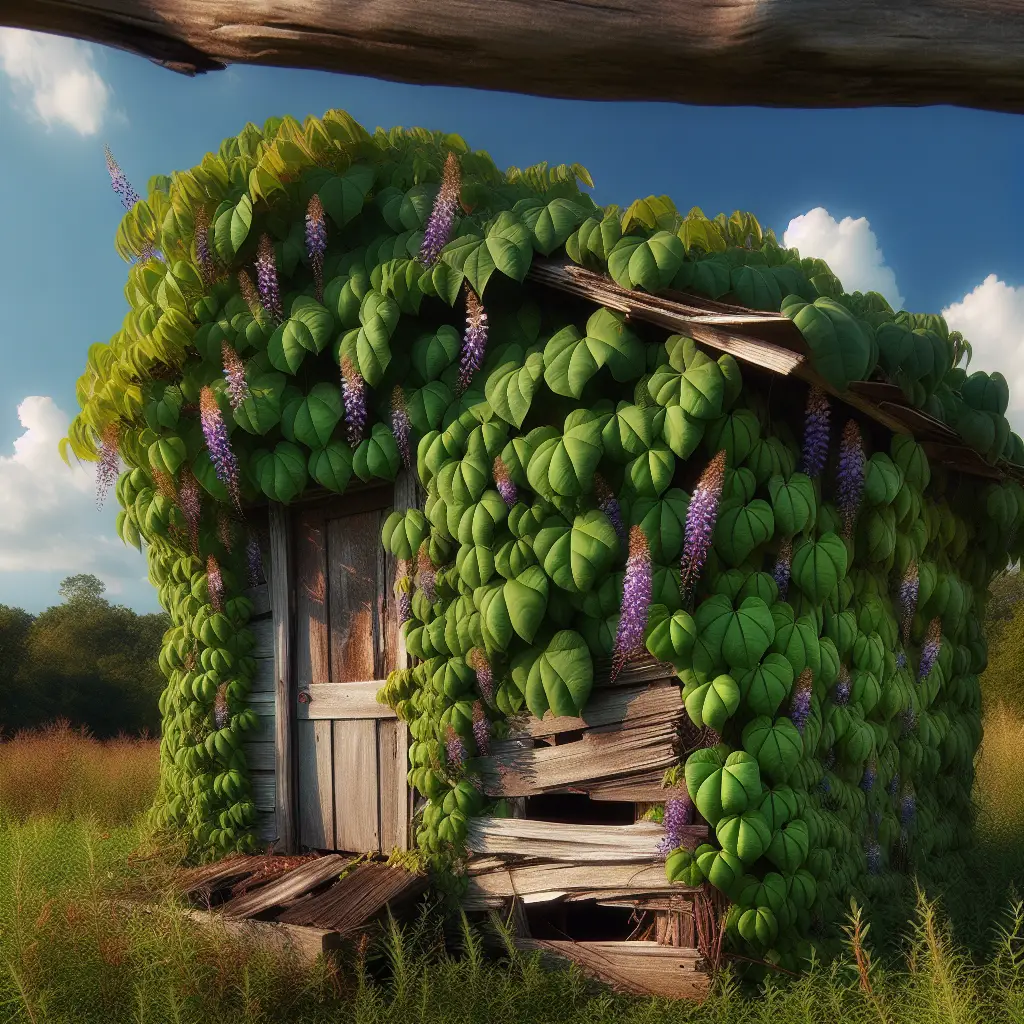
When discussing a Kudzu invasion, it’s crucial to recognize its extraordinary growth rate, which can be up to a foot a day during the peak of its growing season. This rampant growth allows Kudzu to overtake other vegetation and even buildings, earning it the nickname “the vine that ate the South.”
Identifying Kudzu
Spotting kudzu might seem straightforward due to its rapid coverage of landscapes, but proper identification is key to effective management. Kudzu leaves are compound, with three broad leaflets, the middle of which has a notably longer stalk. The vines bear purple, fragrant flowers in the summer and flat, hairy seed pods in the fall.
One of Kudzu’s most distinguishing features is its large tuberous roots, which can be as thick as a person’s arm and weigh as much as 400 pounds. This extensive root system makes Kudzu resilient and challenging to eradicate.
Kudzu’s Impact on Ecosystems
Environmental concerns associated with Kudzu are profound. It smothers other plants and trees under a blanket of leaves, blocking their access to sunlight. This rapid overgrowth disrupts local ecosystems, diminishes biodiversity, and hampers forestry operations.
In addition to its ecological impact, Kudzu also poses economic threats. It can damage power lines and buildings due to its sheer mass and can be quite costly to manage on both private and public lands.
Methods of Control and Eradication
Controlling Kudzu is a multifaceted endeavor requiring persistence and a sound strategy. Physical removal, grazing, herbicide application, and biological control are all options in the battle against this invasive plant.
Manual removal involves cutting or mowing the vines, which can weaken the plant when done regularly over several growing seasons. But for many, the significant labor involved makes this a less practical option, especially over large areas.
Herbicide Solutions
Those seeking chemical intervention often turn to herbicides. One widely reviewed product is Roundup QuikPRO herbicide, known for its effectiveness on Kudzu. Users report that following the proper dilution instructions is vital to its efficacy, suggesting application in the growing season when Kudzu is most vulnerable.
However, care must be taken when using chemicals. Herbicides can affect non-target plants and require safety precautions during application. Moreover, the environmental impact of long-term herbicide use is a consideration many take seriously.
Find This and More on Amazon
Biological Control
Another interesting angle in the fight against Kudzu lies in biological control—a method which utilizes natural predators, pathogens, or competitors to reduce the invasive species’ population. The Kudzu bug, for example, has been studied for this purpose. Though it feeds on Kudzu, releasing these insects must be considered with caution as they could negatively impact other, non-target species or crops.
This nuanced balance of risks and benefits illustrates why biological control is an area of ongoing research and not yet a widely embraced solution against Kudzu.
Mechanical and Cultural Control
Mowing and grazing can be effective against Kudzu, especially as part of an integrated management approach. Regular cutting forces the plant to use stored root energy to regrow, eventually depleting its resources. Grazing animals like goats and sheep find Kudzu palatable and can help control its spread through persistent grazing.
This method not only suppresses Kudzu but can also benefit the grazers as a food source, offering an eco-friendly control alternative that harmonizes with sustainable agricultural practices.
Selecting the Right Approach
The optimal strategy for tackling Kudzu depends on various factors, including the size of the infested area, the degree of the invasion, and environmental considerations. Land managers and property owners must weigh the pros and cons of each method to devise a tailored plan that’s effective and environmentally conscious.
It’s typically most effective to employ multiple methods in a layered approach to control and eradicate Kudzu, often starting with mechanical means to reduce the biomass and following up with herbicides to kill the roots.
Preventative Measures
For land not yet affected by Kudzu, prevention is the best strategy. Monitoring land for early signs of Kudzu growth, maintaining healthy native vegetation, and quick action to remove any initial growth are all crucial steps in preventing an invasion.
Public education on the impact of Kudzu and the importance of early detection and eradication can also play a significant role in preventing the spread of this invasive vine.
Community Engagement in Combating Kudzu
Tackling an invasive species like Kudzu is not just a task for individual landowners — it requires a community effort. Local groups can organize eradication days, wherein volunteers come together to help remove Kudzu from public spaces and educate others about the plant.
These events not only help control the spread but also strengthen community bonds and create a collective sense of responsibility towards maintaining local ecosystems.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Since eradicating Kudzu is a long-term battle, it’s essential to develop sustained management plans. Establishing protocols for regular monitoring and quick response to new growth can prevent Kudzu from re-establishing a foothold after initial efforts.
Adequate funding and resources for ongoing control measures are key, and engaging with local environmental agencies for support and guidance can provide additional expertise and manpower.
The Role of Technology in Kudzu Eradication
Incorporating technology can augment the effectiveness of Kudzu control strategies. Drones and satellite imagery offer innovative ways to monitor large areas for Kudzu presence, enabling a swift and targeted approach to managing outbreaks.
GIS (Geographic Information Systems) and mapping software also play a significant role in tracking the spread and aiding in the strategic planning of control efforts.
Research and Advances in Kudzu Control
Ongoing research is critical for discovering new and better ways to fight Kudzu invasions. Scientists continue to explore the use of more specific herbicides, alternative biological agents, and other innovative methods to target the resilient vine without harming native species.
Keeping abreast of the latest research findings and integrating them into management strategies ensures the use of the most effective, state-of-the-art tactics against Kudzu.
Land Restoration Post-Kudzu Eradication
Once Kudzu is removed, rehabilitating the land is vital to prevent other invasive species from taking over. Planting native vegetation that competes well against invasives can secure the ecosystems and promote biodiversity.
Land managers can consult with local experts on the best native species for their area. Native plant societies and county extension services often provide valuable resources and advice for restoration projects.
Impact of Climate Change on Kudzu Spread
Changing climatic conditions can affect the spread of invasive plants like Kudzu. Warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns could potentially expand the areas at risk for Kudzu invasion.
Understanding these trends will require adjusting management techniques and possibly anticipating new regions of growth, which will demand a proactive approach to control efforts.
Collaboration with Professional Services
For those facing severe Kudzu invasions, professional services may be necessary. These companies offer specialized knowledge and equipment, such as high-capacity sprayers for herbicide application or heavy machinery for large-scale removal.
It’s essential to select a service with experience in invasive plant management and a track record of effective Kudzu eradication. Remember, professional intervention can be costly, so weigh this option carefully against the severity and scale of the infestation.
Cultural Context and Utilizing Kudzu
While Kudzu is a problematic invasive, it’s worth noting that in some cultures, parts of the plant are utilized for food and medicine. Roots, leaves, and flowers can be harvested for various uses — a practice which, if carefully managed, might also contribute to its control.
Still, such uses require a deep understanding of Kudzu’s growth behavior to avoid inadvertently promoting its spread. When managed ethically and sustainably, utilizing Kudzu could become part of an integrated control strategy.
Monitoring Success and Remaining Vigilant
Successfully reducing Kudzu cover is an achievement, but ongoing vigilance is crucial. Regularly assessing the affected areas and documenting successes and setbacks guides future management efforts and can serve as a case study for others tackling Kudzu in their region.
Maintaining thorough records also supports scientific research and can contribute to developing more efficient eradication methods in the long term.
Conclusion: Harnessing a Multi-Pronged Approach
Ultimately, the key to combatting Kudzu lies in a multifaceted approach that combines mechanical, chemical, and biological methods with community engagement, research, and restoration initiatives. By remaining informed, proactive, and persistent, there is hope for reclaiming landscapes dominated by this aggressive vine.
Remember, while Kudzu poses significant challenges, it also provides opportunities for communities to come together in stewardship of the environment, forging partnerships and knowledge that last well beyond the battle against one invasive species.
“`html
Support Systems for Those Battling Kudzu
For individuals and communities engaged in the fight against Kudzu, support systems are invaluable. This could take the form of forums, local groups, or government-sponsored programs that provide advice, resources, and moral support.
Networking with others facing similar challenges allows for the exchange of tips and tactics that have proven effective, and can foster a sense of solidarity in this ecological struggle.
Financial Assistance for Kudzu Eradication
Financial aid, in the form of grants or subsidies, may be available to landowners contending with pervasive Kudzu invasions. These funds can help cover the cost of herbicides, professional services, and other expenses associated with control and removal efforts.
Investigating local, state, and federal resources can uncover financial support options, making the daunting task of Kudzu eradication more manageable.
Personal Experiences and Case Studies
Personal accounts of dealing with Kudzu can provide unique insights and inspire strategies for others. Case studies often highlight both successes and challenges, paving the way for improved practices in managing this invasive species.
Reading and sharing these stories builds a repository of real-world knowledge that can be instrumental in guiding both current and future eradication efforts.
Conclusion: Embracing an Adaptive Mindset
In conclusion, addressing the Kudzu problem is a complex endeavor requiring a comprehensive and adaptable approach. The resilience of Kudzu means that strategies must evolve as we learn more about the plant and as environmental conditions change.
By staying informed, utilizing a wide array of control methods, and working together as communities, we have a better chance of curbing the pervasive spread of Kudzu and protecting our ecosystems and infrastructures from its impacts.
“`
Shop more on Amazon