The Science of Water pH and Its Impact on Plant Health
Updated June 22, 2024 at 1:20 pm
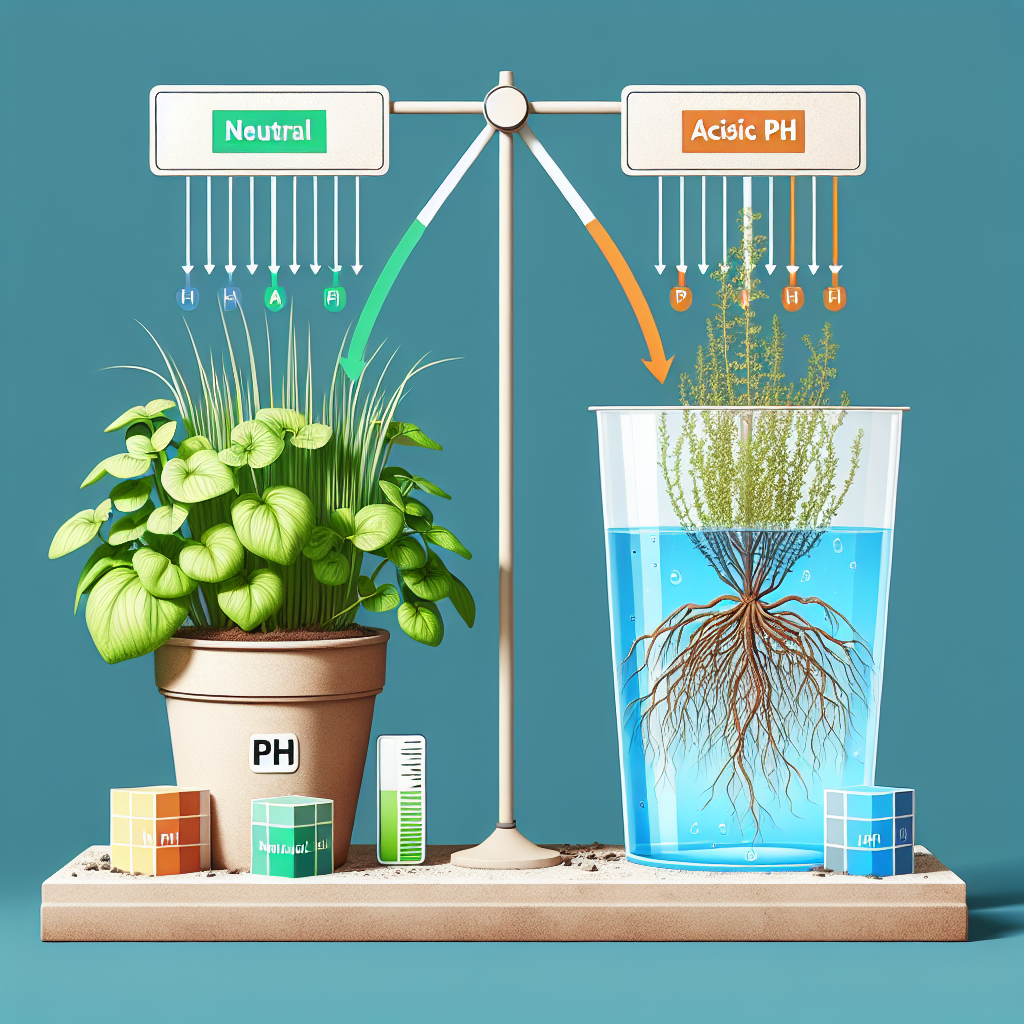

Understanding Water pH for Optimized Plant Health
When it comes to nurturing a thriving garden or maintaining healthy indoor plants, the pH level of your water can make all the difference. pH stands for “potential hydrogen” and measures the acidity or alkalinity of a substance on a scale from 0 to 14. Pure water is neutral at a pH of 7, levels below 7 indicate acidity, and levels above 7 are considered alkaline.
The Role of pH in Plant Nutrient Uptake
Plants have specific pH ranges that optimize the availability of essential nutrients in the soil. Generally, a slightly acidic pH of 6 to 6.5 is ideal for most plants because it allows for optimal nutrient absorption. If the pH is too high or too low, plants might exhibit nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, despite the presence of sufficient nutrients in the soil.
Identifying pH-related Problems in Plants
If you might be seeing poor growth, discolored leaves, or a lack of flowering, it could indicate a pH issue. Yellowing leaves can signal iron deficiency commonly seen in high pH soils, while stunted growth can result from aluminum or manganese toxicity at low pH levels.
Testing and Adjusting Soil pH
Regularly testing your soil’s pH can help you maintain the balance your plants need. You can use pH testing kits or meters. Based on the results, you can add lime to raise pH or sulfur to lower it. Even compost can help buffer soil pH to create a more neutral environment for your plants.
pH Levels in Hydroponics and Aquaponics
In hydroponic or aquaponic systems, water pH is equally crucial as nutrients are provided directly in the water solution. Such systems often require more frequent pH testing and adjustments to ensure plants remain healthy.
The Importance of Using the Right Water
Tap water can vary in pH, which can affect plant health over time. Using filtered or distilled water with a neutral pH can be beneficial. But keep in mind, relying solely on distilled water can potentially lead to a lack of essential minerals.
Choosing pH Adjusters and Monitors
- General Hydroponics pH Control Kit: This kit is a popular choice for managing pH levels in hydroponic systems. It includes pH Up and pH Down solutions, along with a test indicator for easy pH monitoring. It’s said that people appreciate its simplicity and effective results.
Find This and More on Amazon
Natural Methods of Adjusting pH
For those who prefer natural solutions, incorporating certain organic matter into your soil can modulate pH levels. For example, peat moss can help to lower pH, while crushed eggshells can raise pH.
pH as a Factor in Pest and Disease Resistance
Maintaining the right pH can also enhance a plants defense against certain pests and diseases. Healthy plants with optimum pH balance are more resilient and less susceptible to issues like root rot and fungal infections.
Impact of Water Quality on pH
Water quality is paramount as contaminants and minerals in water can influence the pH. Softened water, for example, often has a higher sodium content, which can lead to an increase in pH and potentially harm plants sensitive to high pH levels.
Understanding the pH Preferences of Popular Plants
Research the pH preferences of your garden favorites or indoor companions. Azaleas and blueberries thrive in more acidic soils, while vegetables like broccoli and cabbage prefer a slightly alkaline soil.
Professional Soil Analysis
If you are serious about the science of soil pH, consider a professional soil analysis from a local extension office or a dedicated laboratory. They can provide detailed guidance tailored to your specific garden or indoor plant setup.
Potential Effects of Climate on Soil pH
Climate factors such as rainfall can impact soil pH over time, usually leading to increased acidity. Regular pH testing can alert you to any gradual changes so you can adjust your soil amendments accordingly.
Comprehensive Guide to pH Meters and Test Kits
For accuracy in pH testing, it’s essential to invest in a reliable pH meter or test kit. One product that stands out is the Bluelab pH Pen, which is touted for its precision and ease of use. It’s a pocket-sized, handheld pH meter offering a quick digital readout of pH levels. Users often highlight how this device is a game-changer for their routine checks, noting its durability and user-friendly calibration process.
- Digital Accuracy: The Bluelab pH Pen provides rapid and accurate pH readings, which can be crucial for quickly diagnosing and correcting pH issues.
- Convenience: With its compact design, it’s easy to carry around the garden or grow space, making pH testing more convenient.
- Calibration and Maintenance: Calibrating the pH pen is straightforward, with instructions from Bluelab that many find helpful. Regular calibration is necessary to maintain accuracy.
Find This and More on Amazon
Promoting Soil Health Beyond pH
While pH is significant, overall soil health can’t be ignored. A balanced ecosystem within the soil not only supports proper pH but also contributes to nutrient cycling and disease suppression. Organic methods such as adding compost or using cover crops can enhance soil structure and nourish beneficial microorganisms.
The Role of Fertilizers in Managing pH
Fertilizers are not just about boosting nutrients; they also influence soil pH. For instance, ammonium-based fertilizers can lower soil pH over time. Conversely, lime-based fertilizers can make the soil more alkaline. It’s essential to choose the right type of fertilizer based on your plant’s pH preferences and soil conditions.
Advanced pH Management Techniques
Beyond simple amendments, there are advanced techniques for managing pH. For example, in certain soil types, foliar sprays can be used to address micronutrient deficiencies due to pH imbalances. These are highly targeted treatments and should be employed with precision.
Seasonal Variations in pH Balance
Be aware that pH levels can fluctuate with the seasons. In the spring, soil may be more acidic due to organic matter decomposition, while in the dry summer months, the pH might skew more alkaline. Adjust your care routine accordingly for year-round plant health.
The Future of pH Technology and Plant Care
Scientific developments continue to advance pH technology. Innovations such as smart soil sensors and automated pH adjusters could streamline the process, making optimal pH management easier than ever for both hobbyists and commercial growers.
Understanding Water pH and Its Impact on Plant Health
pH is a critical factor in plant health, and understanding it can make a significant difference in achieving a lush, vibrant garden or indoor plant collection. By regularly testing your water and soil, adjusting pH levels when necessary, and staying informed of each plant’s needs, you’ll create an environment where plants can flourish. Always approach pH management with careful consideration for your plants’ specific needs – it’s the balance between science and nature that engenders a healthy, happy plant life.
Practical Tips for Monitoring and Adjusting pH
Monitoring and adjusting the pH of your soil or hydroponic solution does not have to be daunting. Start by using a simple pH test strip or a digital pH meter for more accurate readings. When adjusting pH, make small changes and wait for the plants to respond before adding more adjusters. Always follow the instructions on the pH adjusters precisely, as over-adjusting can create a stressful environment for your plants.
Effect of Local Water Sources on pH
Your local water source plays a significant role in your garden’s pH. Some regions have naturally hard water that is high in minerals and can raise the soil’s pH. Conversely, soft water might contain more acid, potentially lowering soil pH. It is beneficial to have your water tested so that you can make informed decisions on pH adjustment. Using rainwater as an alternative can be a neutral pH option for your garden.
Common Misconceptions About Water pH and Plants
One common misconception is that water pH does not matter if you are using a good quality potting mix or fertilizer. However, the pH of your water can significantly influence the effectiveness of your fertilizers and the health of your soil or other growing media. Another myth is that all plants thrive at a neutral pH level, but many plants have specific pH requirements that differ from this.
The Synergy between pH and Other Soil Qualities
While the focus is on pH, it’s essential to understand that pH interacts with soil texture, organic matter content, and microbiological activity to influence plant health. For example, sandy soils may require different pH adjustments than clay soils due to their differing buffering capacities. Similarly, organic-rich soils tend to be more resilient to pH fluctuations.
How to Deal with Extreme pH Levels
Extreme pH levels can be detrimental to plant health and may sometimes require more than simple amendments. For highly acidic soils, repeated applications of lime or a faster-acting lime alternative like calcium carbonate may be necessary. In contrast, for overly alkaline soils, elemental sulfur or sulfates can be used to increase acidity over time. Always integrate amendments gradually and carry out regular pH testing.
Long-Term pH Management Strategies
Long-term pH management is about balance and anticipation. Cultivating a diverse garden that includes plants with varying pH preferences can buffer against drastic pH changes. Another strategy is to create separate zones in your garden for plants with similar pH requirements, facilitating targeted pH management.
pH and Its Relationship with Soil Organisms
Soil is a living entity, teeming with microorganisms that interact with and are influenced by soil pH. Some beneficial bacteria and fungi thrive in particular pH ranges and play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and plant growth. Meanwhile, harmful organisms might be deterred by maintaining the correct pH levels. Composting and using microbial inoculants can also introduce and nurture beneficial soil organisms.
The Relationship Between Water pH and Fertilizer Efficiency
Fertilizer efficiency greatly depends on the correct water pH. If the pH is not within the proper range, plants may not be able to access the nutrients in fertilizers, rendering them ineffective. Proper pH adjustment ensures that you are not wasting your fertilizers and that your plants are receiving all the possible benefits.
Case Studies: Real-life Examples of pH Correcting Plant Health
Case studies illustrate the real-world impact of pH on plant health. For example, a study on blueberry crops demonstrated that by adjusting soil pH from the initially alkaline levels to the slightly acidic range preferred by blueberries, the growers saw a marked improvement in fruit quality and yield. This underscores the importance of knowing and catering to the specific pH needs of each plant species.
Creating a pH-Friendly Garden Plan
Developing a garden plan with pH in mind can save time and effort in the long run. Collaborate with local nurseries to select plants with similar pH preferences for your garden zones. Prioritize areas that receive the majority of rainfall for acid-loving plants since rainwater can gradually reduce soil pH, and use shade strategically for plants that prefer a more stable pH.
Integrating pH Control into a Holistic Plant Care Routine
Integrating pH control into your regular plant care regimen can result in an overall healthier garden. Add pH testing to your schedule—whether it’s weekly for hydroponics or monthly for soil gardens. When adjusting pH as part of your routine, consider the entire ecosystem, from the beneficial insects to the soil microbiome, to ensure a holistic approach to plant health.
Water pH and Sustainable Gardening Practices
Sustainable gardening practices are becoming increasingly popular, and managing water pH plays a crucial role in these systems. For example, using rainwater catchment systems can provide a source of water with a generally neutral pH, reducing the need for adjustments. Implementing these systems contributes to the overall sustainability and resilience of your garden.
Public Resources and Support for Soil and Water pH Management
Many public resources, such as extension services and local gardening clubs, offer support for soil and water pH management. These organizations can provide soil testing services, workshops, and personalized advice to help you navigate the intricacies of pH balance in your garden.
Final Thoughts on Water pH and Plant Health
Understanding and managing water pH is a fundamental aspect of successful gardening and plant care. Taking the time to learn about your plants’ specific pH requirements and monitoring your water and soil pH can ensure that your garden remains vibrant and productive. Remember, when in doubt, don’t hesitate to reach out to experts or use public resources to gain knowledge. A little pH awareness goes a long way in nurturing a healthy relationship between your plants and their environment.
Shop more on Amazon